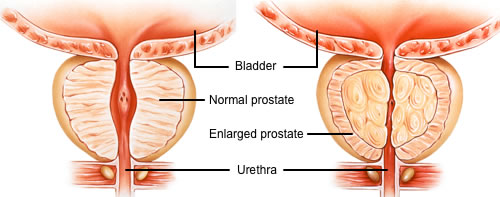
Prostate Enlargement
Overview: Prostate enlargement, also known as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition in aging men where the prostate gland enlarges and can cause various urinary symptoms. While not cancerous, BPH can significantly impact the quality of life due to its effects on urinary function.
Overview: Prostate enlargement, also known as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition in aging men where the prostate gland enlarges and can cause various urinary symptoms. While not cancerous, BPH can significantly impact the quality of life due to its effects on urinary function.
Causes: The exact cause of prostate enlargement is not fully understood, but it is believed to be influenced by hormonal changes, particularly the increase in dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels as men age. Other contributing factors may include genetics, inflammation, and lifestyle factors.
Symptoms of Prostate Enlargement (BPH): The symptoms of BPH are primarily related to urinary function and can vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination:
- Needing to urinate more often, especially at night (nocturia).
- Urgency:
- A sudden, strong urge to urinate.
- Weak Stream:
- Reduced force and caliber of the urinary stream.
- Difficulty Initiating Urination:
- Trouble starting the urine flow.
- Intermittency:
- The urine stream starts and stops during voiding.
- Incomplete Emptying:
- Feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied after urination.
- Straining:
- Effort required to push urine out.
- Urinary Retention:
- In severe cases, the inability to empty the bladder completely, leading to urinary retention.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs):
- Increased risk of UTIs due to incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Diagnosis: Diagnosis is typically based on a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as a digital rectal exam (DRE) and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test. Imaging studies like ultrasound or cystoscopy may also be used to assess the extent of prostate enlargement.