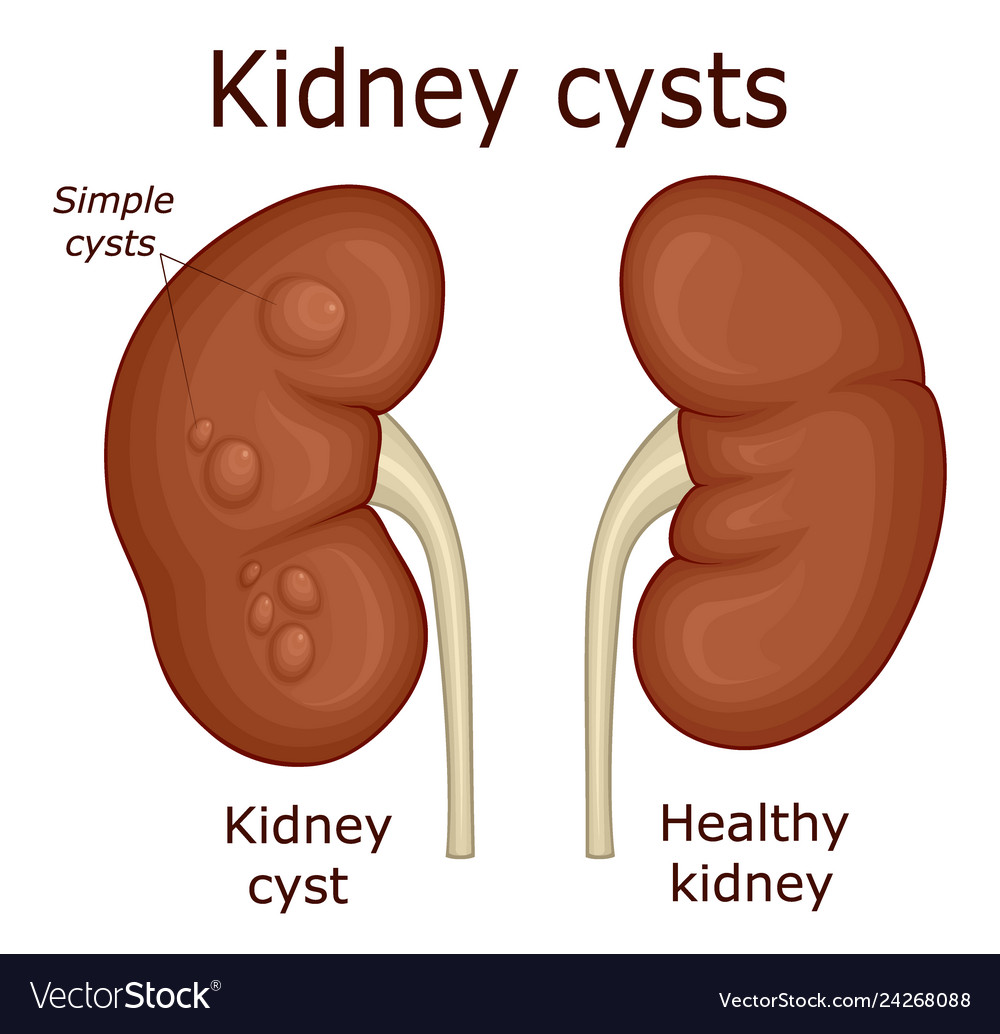
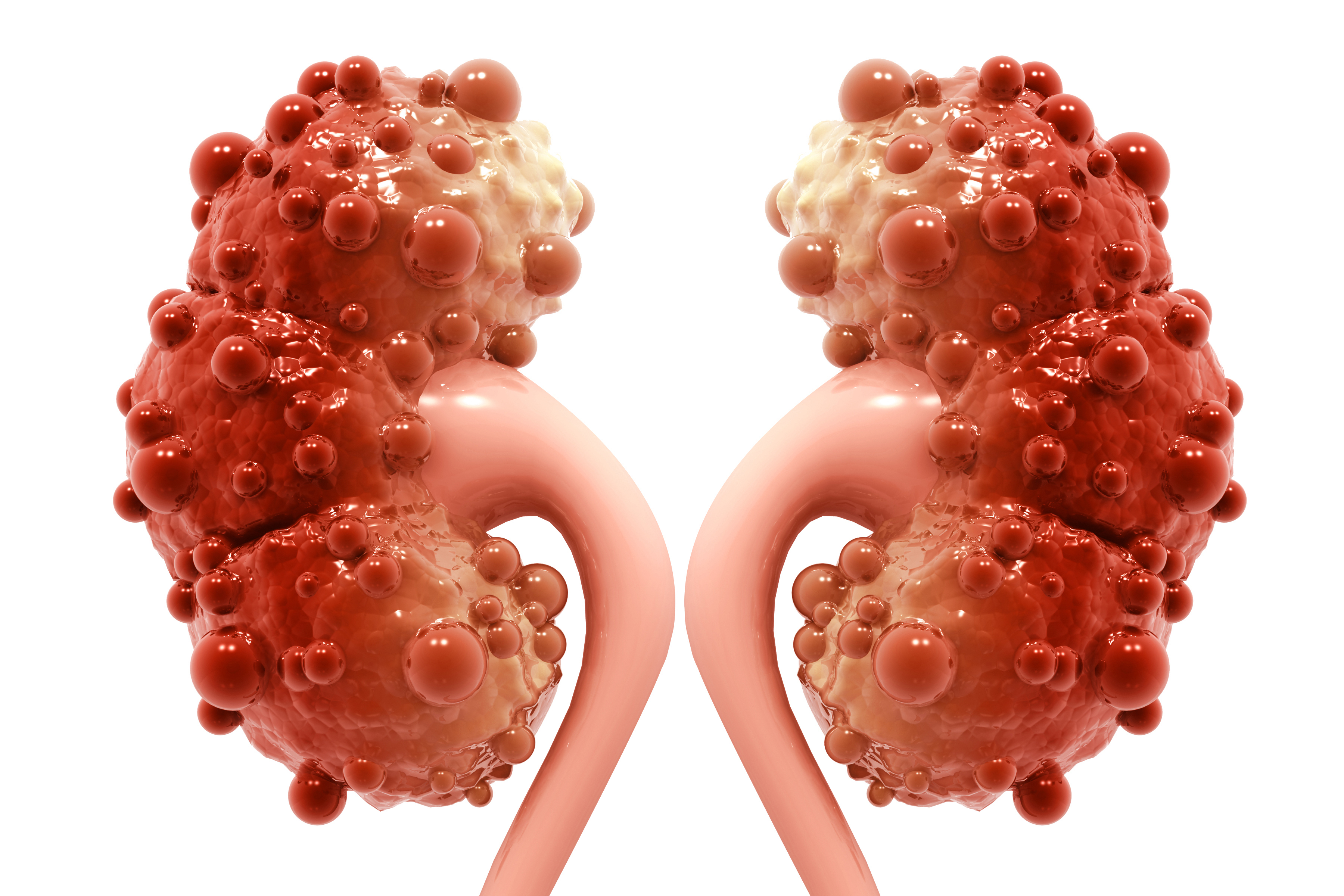
Kidney Cysts
Overview: Kidney cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on or within the kidneys. They are usually noncancerous and may not cause symptoms. While many kidney cysts are benign and harmless, some may lead to complications or indicate an underlying medical condition.
Overview: Kidney cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on or within the kidneys. They are usually noncancerous and may not cause symptoms. While many kidney cysts are benign and harmless, some may lead to complications or indicate an underlying medical condition.
Types of Kidney Cysts:
- Simple Kidney Cysts:
- Most common type.
- Usually round, thin-walled, and filled with clear fluid.
- Often benign and rarely cause complications.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD):
- Genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts in both kidneys.
- Can lead to kidney enlargement, kidney failure, and other complications.
Causes:
- Simple Kidney Cysts:
- Typically develop as a result of aging.
- The exact cause is often unknown.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease:
- Inherited genetic mutations, usually passed down through families.
Symptoms:
- Simple Kidney Cysts:
- Often asymptomatic and discovered incidentally during imaging tests.
- Rarely cause pain or complications.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease:
- Kidney pain or tenderness.
- High blood pressure.
- Frequent urinary tract infections.
- Blood in urine.
- Kidney stones.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort.
Diagnosis:
- Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize and assess the size and characteristics of the cysts.
- Genetic Testing:
- For suspected cases of polycystic kidney disease.
- Blood and Urine Tests:
- To check kidney function, detect blood in urine, and assess for associated conditions.
Prevention:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Regular Monitoring:
For individuals with polycystic kidney disease, regular check-ups and monitoring of kidney function.