Allopecia
Overview: Alopecia refers to hair loss, which can occur on the scalp or other parts of the body. There are various types of alopecia, each with its own set of symptoms and potential causes.
Overview: Alopecia refers to hair loss, which can occur on the scalp or other parts of the body. There are various types of alopecia, each with its own set of symptoms and potential causes.
Types of Alopecia:
- Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness):
- Symptoms: Gradual hair thinning, especially at the crown or temples.
- Cause: Genetic and hormonal factors contribute to this common form of hair loss.
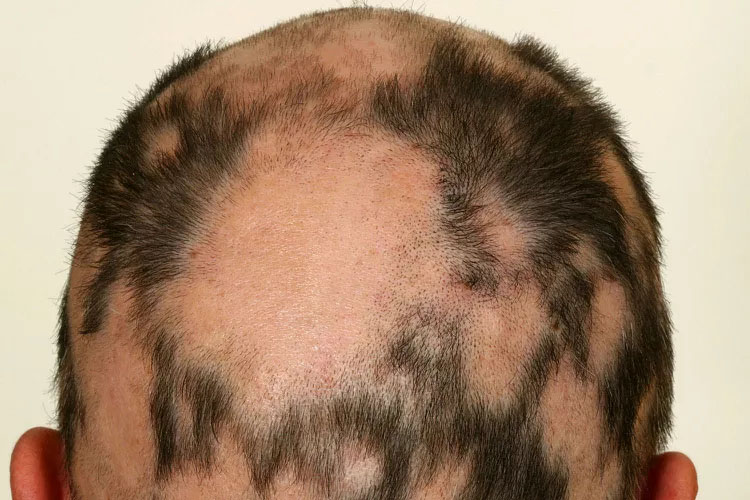
- Alopecia Areata:
- Symptoms: Sudden loss of hair in small, round patches on the scalp or other areas of the body.
- Cause: Autoimmune response where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles.
- Alopecia Totalis:
- Symptoms: Complete loss of hair on the scalp.
- Cause: Similar to alopecia areata, but affecting the entire scalp.
- Alopecia Universalis:
- Symptoms: Total loss of hair on the scalp and body.
- Cause: An advanced form of alopecia areata affecting the entire body.
- Telogen Effluvium:
- Symptoms: Sudden, widespread hair shedding, often triggered by stress, illness, or hormonal changes.
- Cause: Disruption of the hair growth cycle, causing more hair follicles to enter the resting (telogen) phase.
- Trichotillomania:
- Symptoms: Hair loss due to compulsive hair-pulling, often associated with stress or anxiety.
- Cause: Behavioral disorder linked to psychological factors.
Causes of Alopecia:
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in androgenetic alopecia, the most common form of hair loss.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Disorders like alopecia areata involve the immune system mistakenly attacking hair follicles.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as those occurring during pregnancy, childbirth, or menopause, can contribute to hair loss.
- Medical Conditions: Certain illnesses, like thyroid disorders or lupus, may lead to hair loss.
- Medications: Some drugs, including chemotherapy drugs, anticoagulants, and certain antidepressants, can cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Stress and Trauma: Physical or emotional stress, major surgeries, or traumatic events can trigger telogen effluvium.