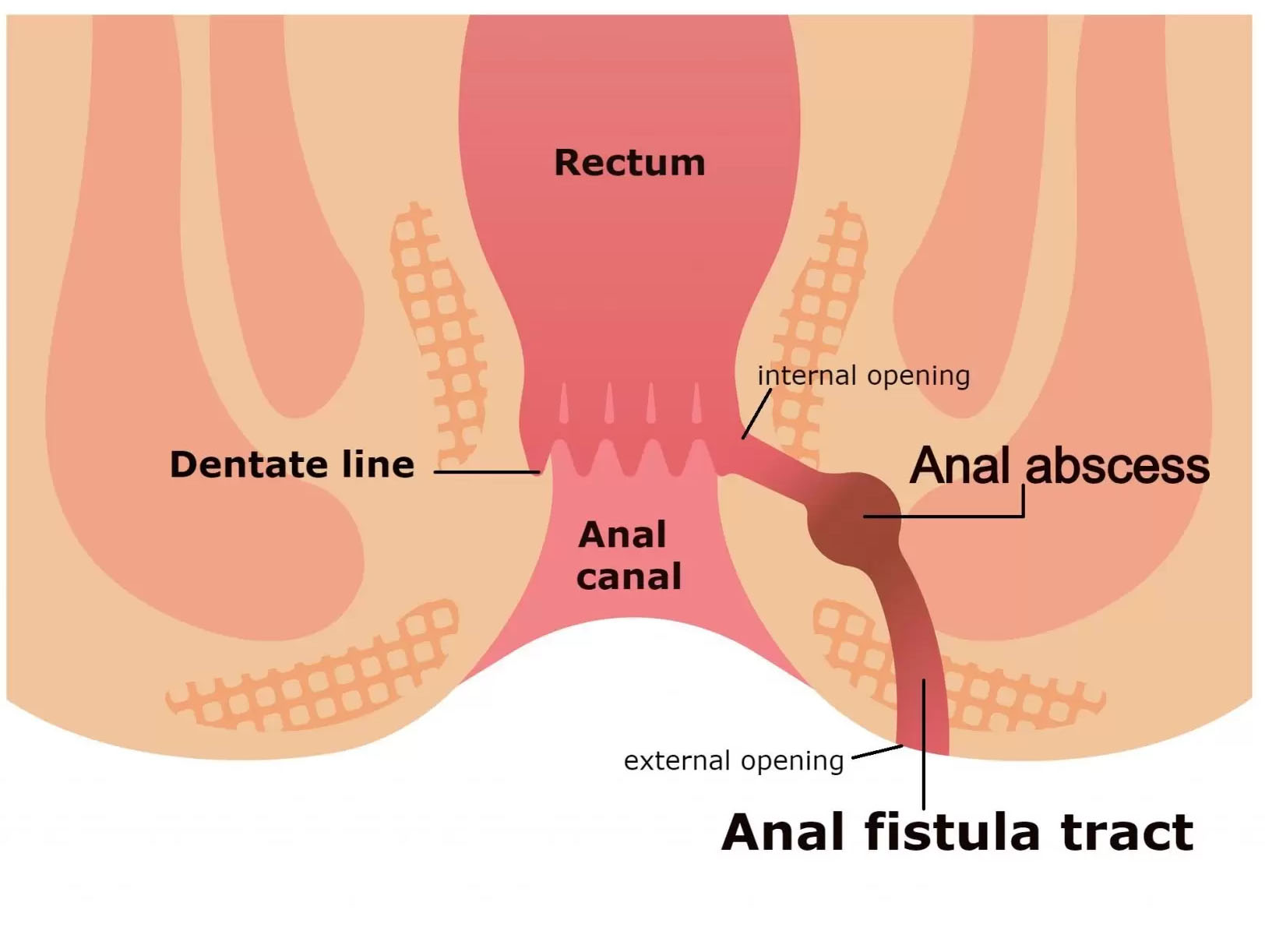
Anal Fistula
Overview: An anal fistula is an abnormal tunnel or channel that forms between the anal canal or rectum and the skin near the anus. It usually results from an infection or abscess in the anal glands. Anal fistulas can cause pain, discomfort, and drainage of pus, and they often require medical intervention.
Causes:
- Anal Abscess:
- An infection in the anal glands can lead to the formation of an abscess, which may later develop into a fistula.
- Crohn's Disease:
- Inflammatory bowel disease, particularly Crohn's disease, is associated with a higher risk of anal fistulas.
- Infection:
- Bacterial infections, such as tuberculosis or sexually transmitted infections, can contribute to fistula formation.
- Trauma:
- Injury to the anal or rectal area, such as during childbirth or anal surgery.
- Diverticulitis:
- Inflammation or infection of diverticula (small pouches) in the colon.
Symptoms:
- Pain and Discomfort:
- Persistent pain, swelling, or tenderness in the anal region.
- Pus or Fluid Drainage:
- Continuous or intermittent discharge of pus or fluid near the anus.
- Redness and Swelling:
- Red and swollen tissue around the anal opening.
- Itching and Irritation:
- Itching and irritation in the anal area.
- Fever:
- In some cases, fever may be present, especially if there is an associated infection.
Diagnosis:
- Physical Examination:
- A healthcare professional will visually inspect the anal area and may perform a digital rectal examination.
- Imaging Studies:
- Imaging techniques, such as MRI or ultrasound, may be used to visualize the fistula tract.