Fatty Liver
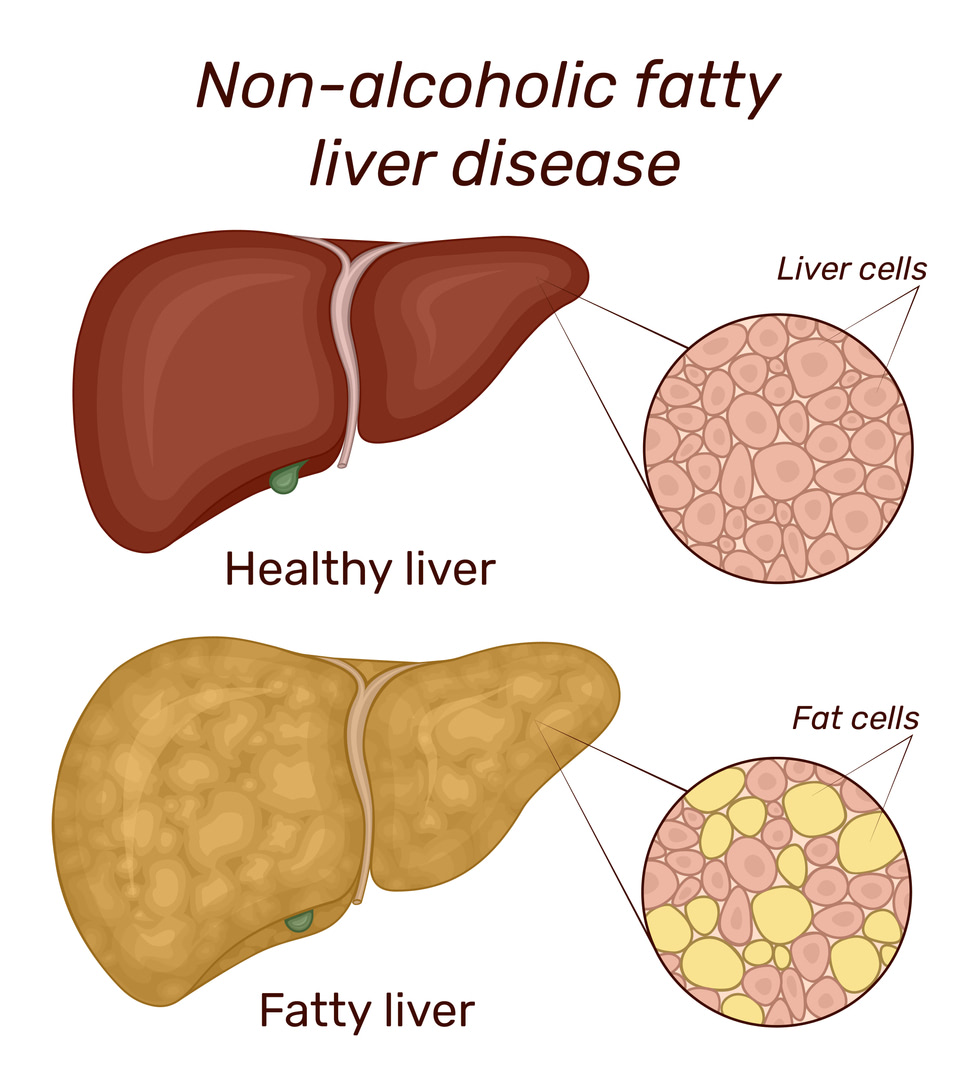
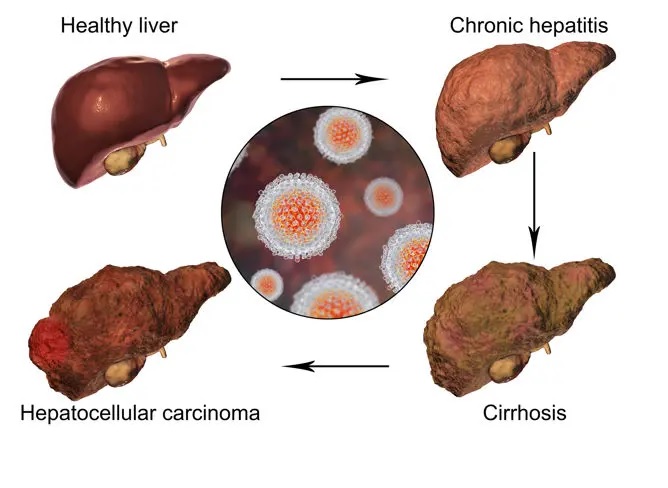
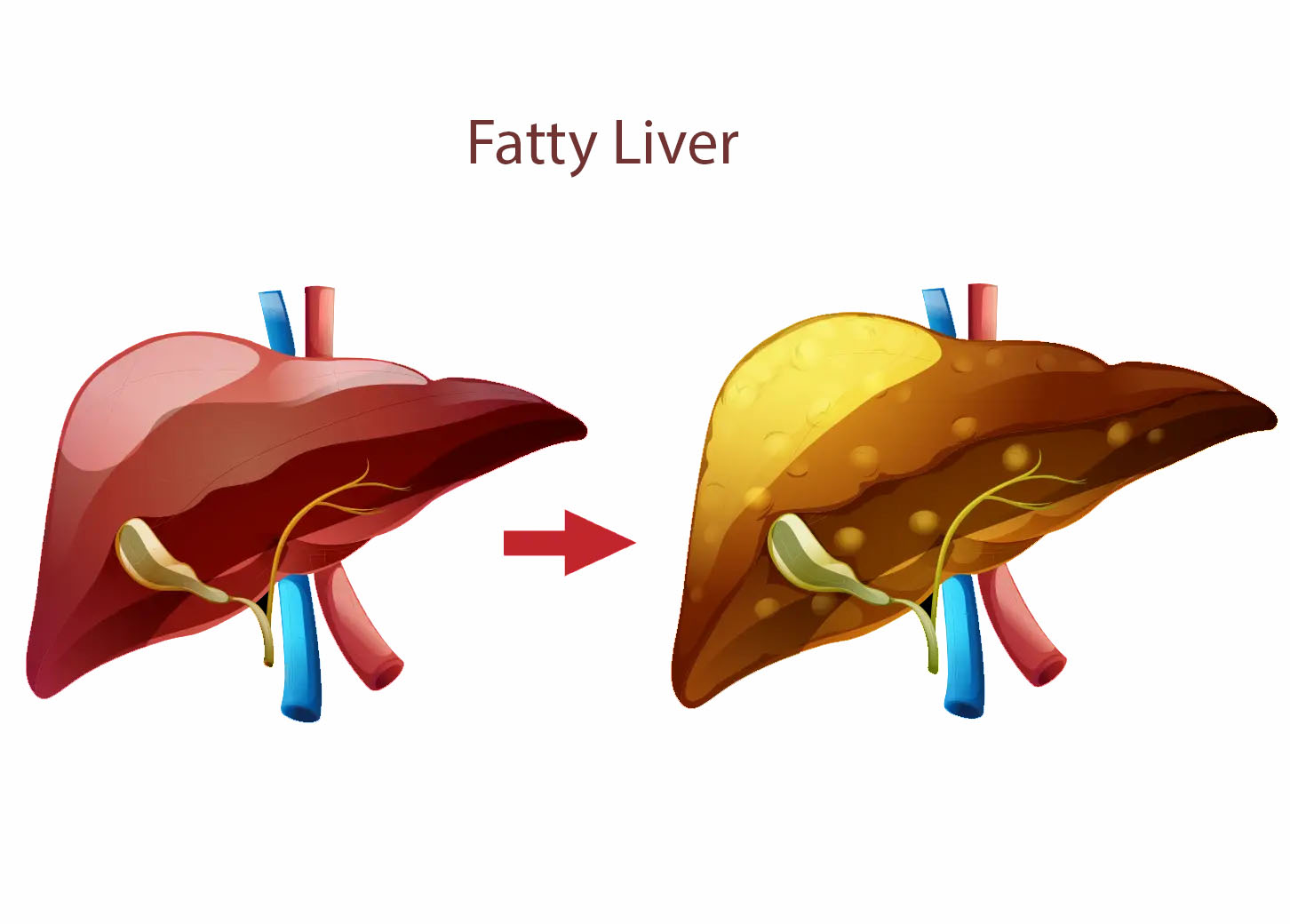
Overview: Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells. While a small amount of fat in the liver is normal, excessive fat accumulation can lead to inflammation and impaired liver function. Fatty liver disease is often categorized into two main types: alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Causes:
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD):
- Caused by excessive alcohol consumption over an extended period, leading to fat accumulation in the liver.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
- Associated with factors other than alcohol consumption, including:
- Obesity: Excess body weight, especially abdominal fat.
- Insulin Resistance: A condition where cells don't respond effectively to insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Diabetes is a risk factor for NAFLD.
- High Blood Lipids: Elevated levels of triglycerides or cholesterol.
Symptoms:
- Usually Asymptomatic:
- Early stages may not present noticeable symptoms.
- Fatigue:
- Generalized tiredness and weakness.
- Abdominal Discomfort:
- Discomfort or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Enlarged Liver:
- In some cases, the liver may become enlarged.
- Elevated Liver Enzymes:
- Blood tests may reveal elevated levels of liver enzymes.
Diagnosis:
- Liver Function Tests:
- Blood tests to assess liver function and enzyme levels.
- Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the liver and assess fat content.
- Liver Biopsy:
- A tissue sample may be taken to assess the extent of liver damage.
Management:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight loss through a combination of a healthy diet and regular exercise.
- Dietary Changes:
- Limiting intake of saturated fats, sugars, and refined carbohydrates.
- Physical Activity:
- Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and aids in weight management.
- Management of Underlying Conditions:
- Controlling conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol.
- Alcohol Moderation or Abstinence:
- For alcoholic fatty liver disease, reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption is crucial.