Leucorrhoea
Overview: Leucorrhoea, also known as vaginal discharge, is a common condition in which there is an abnormal discharge from the female genital tract. While a certain amount of vaginal discharge is normal and serves as a protective mechanism, changes in color, consistency, or odor may indicate an underlying issue.
Causes:
- Normal Physiological Changes:
- Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or ovulation.
- Infections:
- Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, such as yeast infections or bacterial vaginosis.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs):
- Infections like chlamydia, gonorrhea, or trichomoniasis can cause abnormal discharge.
- Poor Hygiene:
- Inadequate genital hygiene can contribute to infections.
- Irritation or Allergic Reactions:
- Contact with irritants, such as certain soaps, detergents, or contraceptive devices.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):
- Inflammation of the reproductive organs, often due to untreated infections.
- Cervical Erosion:
- Erosion of the cervix, which can cause increased vaginal discharge.
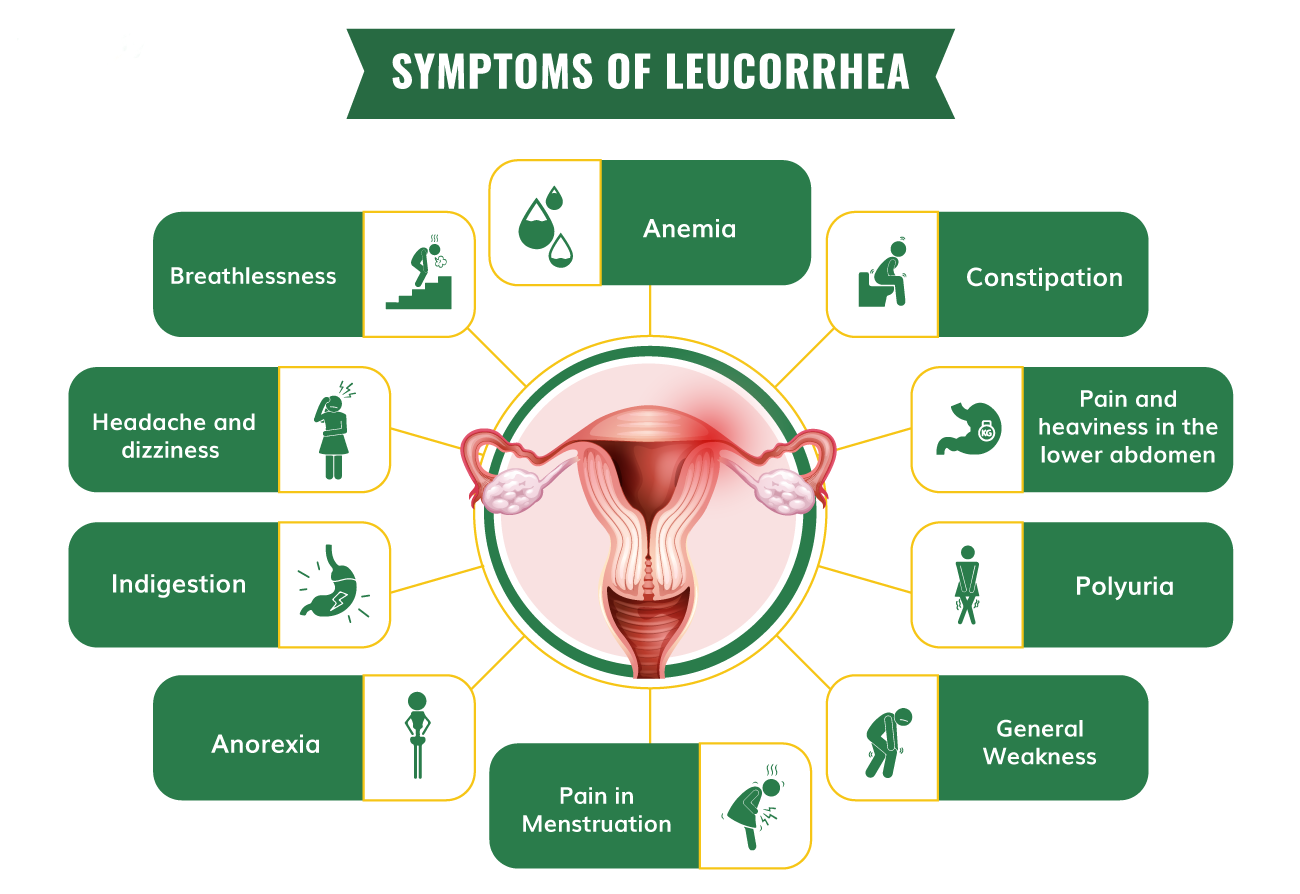
Symptoms:
- Abnormal Vaginal Discharge:
- Changes in color, consistency, or odor of the discharge.
- Itching or Irritation:
- Itching in the genital area.
- Burning Sensation:
- Discomfort or burning sensation during urination.
- Pelvic Pain:
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic region.
- Redness or Swelling:
- Redness or swelling of the genital tissues.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical Examination:
- A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination to assess symptoms.
- Swab Test:
- Taking a sample of the vaginal discharge for laboratory analysis.
Management:
- Probiotics:
- To restore the balance of healthy bacteria in the vagina.
- Avoiding Irritants:
- Identifying and avoiding substances that may cause irritation.
- Hygiene Practices:
Maintaining good genital hygiene.